| NEOPENTYL GLYCOL | ||
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | ||
| CAS NO. |
126-30-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
204-781-0 |
|
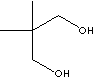
| FORMULA | HOCH2C(CH3)2CH2OH | |
| MOL WT. | 104.15 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2905.39 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 3200 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS |
2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-propanediol; Dimethylolpropane; |
|
| 2,2-dimethylpropane-1,3-diol; 2,2-Dimethyltrimethylene glycol; Neopentanediol; Neopentylene glycol; Dimethyltrimethylene glycol; Hydroxypivalyl alcohol; 1,3-Dihydroxy-2,2-dimethylpropane; 2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-dihydroxypropane; NPG; | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | White Flake and Molten form at 150 C | |
| MELTING POINT | 124 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 210 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.06 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble. (Soluble in methanol, aceton) |
|
| pH | ||
| VAPOR PRESSURE | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
375 C |
|
| FLASH POINT |
107 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Glycol: any of a class of organic chemicals characterized by having separate two
hydroxyl (-OH) groups, contribute to high water solubility, hygroscopicity and
reactivity with many organic compounds, on usually linear and aliphatic carbon
chain. The general formula is CnH2n(OH)2 or (CH2)n(OH)2. The broadened names
include diols, dihydric alcohols, and dihydroxy alcohols. Ethylene glycol,
HOCH2CH2OH, is the simplest member of the glycol family. Mono-, di- and
triethylene glycols are the first three members of a homologous series of
dihydroxy alcohols. Propylene glycol prepared by hydrolysis of propylene oxide
and widely used as an ingredient of antifreeze and humectant in cosmetics is
1,2-propanediol indicating the two hydroxyl group position at 1,2, while
trimethylene glycol is 1,3-propanediol with two hydroxyl group on the primary
carbon atoms.
Neopentylglycol (called structurally 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediol or dimethyltrimethylene glycol) is a diol which features unique chemical structure. It has 1,3-position two hydroxyl groups on the primary carbon atom for rapid esterification reaction and two methyl groups, instead of the usual hydrogen atoms, on the alpha-carbon atom for the high chemical and thermal stability. It is a white crystalline solid; partially soluble in water; soluble in oxygenated solvents and completely soluble in alcohol. Neopentylglycol and its derivatives have the applications in the fields including water based coatings, magnetic coatings, gel coats, powder coatings, high solid systems, coil coatings, multilayer coatings (on alkyds, epoxy, polyester and poly urethane resins). It is also used as an intermediate for the synthesis of lubricants, plasticizers, adhesives, mortar or cement systems, photographic materials, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, fragrances, fibre lubricants antistatic agents, fabric softeners, vibration dampeners. Ne(o)- is the prefix added to the name of a related older compound to denote a new or recent compound, typically more branched chains in the normal structure. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
White flake and molten form at 150 C | |
|
CONTENT |
99.0% min |
|
| MELTING POINT |
123 C min |
|
| OH CONTENT |
32.0% min |
|
| CLARITY |
15 max |
|
|
ASH |
0.01% max |
|
| COLOR , APHA |
20max ( 50%) |
|
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in Bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
|
| UN NO. |
|
|
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 41, Safety Phrases: 22-24-26 | ||
| PRICES | ||